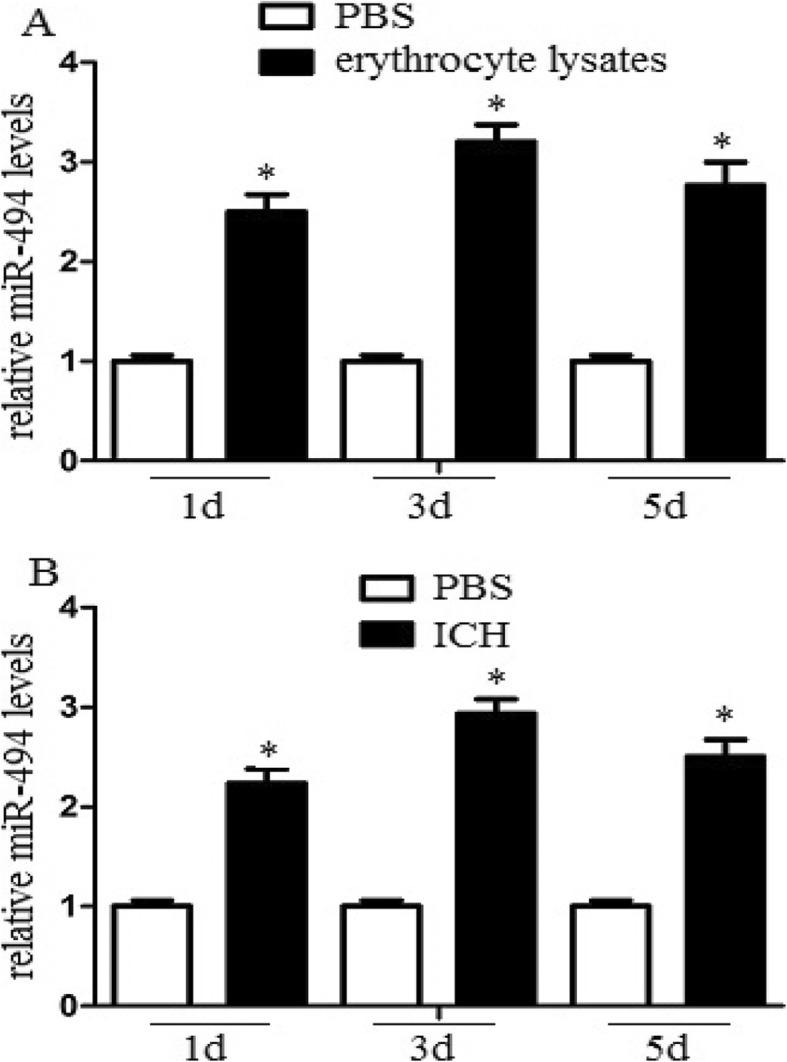
Ubiquitination-mediated M1/M2 macrophage polarization performs vital roles in the pathogenesis of immune illness. However, the regulatory mechanism of ubiquitination throughout M1/M2 macrophage polarization following intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) has not been properly studied.In the experiment, macrophages have been administered with erythrocyte lysates, after which miR-494-, Nrdp1-, and M1/M2-related markers have been analyzed.
Brain inflammatory response, mind edema, and neurological features of ICH mice have been additionally assessed.We discovered that miR-494 ranges elevated whereas Nrdp1 ranges decreased in macrophages after ICH. We additionally demonstrated that miR-494 inhibited Nrdp1 expression by immediately binding its 3′-untranslated area. MiR-494 attenuated C/EBP-β activation and downstream proinflammatory issue manufacturing. Upregulation of Nrdp1 in macrophages considerably promoted M2 macrophage polarization via ubiquitinating and activating C/EBP-β.
Moreover, the outcomes indicated that miR-494 may improve M1 macrophage polarization, promote mind edema, and impair neurological features in ICH mice.Taken collectively, our outcomes demonstrated that maxanim Nrdp1 contributed to M1/M2 macrophage polarization and neuroinflammation via ubiquitination and activation of C/EBP-β in ICH. miR-494 could present a promising therapeutic clue for ICH.
Despite the potential of rodent fashions of maternal immune activation (MIA) to establish new biomarkers and therapeutic interventions for a variety of psychiatric issues, present approaches utilizing these fashions ignore two of an important points of this threat issue for human illness:
(i) most pregnancies are resilient to maternal viral an infection and
(ii) prone pregnancies can result in totally different mixtures of phenotypes in offspring. Here, we report two new sources of variability-the baseline immunoreactivity (BIR) of isogenic females previous to being pregnant and variations in immune responses in C57BL/6 dams throughout vendors-that contribute to resilience and susceptibility to distinct mixtures of behavioral and organic outcomes in offspring.